Medical Terminology Daily (MTD) is a blog sponsored by Clinical Anatomy Associates, Inc. as a service to the medical community. We post anatomical, medical or surgical terms, their meaning and usage, as well as biographical notes on anatomists, surgeons, and researchers through the ages. Be warned that some of the images used depict human anatomical specimens.
You are welcome to submit questions and suggestions using our "Contact Us" form. The information on this blog follows the terms on our "Privacy and Security Statement" and cannot be construed as medical guidance or instructions for treatment.
We have 761 guests and no members online

Jean George Bachmann
(1877 – 1959)
French physician–physiologist whose experimental work in the early twentieth century provided the first clear functional description of a preferential interatrial conduction pathway. This structure, eponymically named “Bachmann’s bundle”, plays a central role in normal atrial activation and in the pathophysiology of interatrial block and atrial arrhythmias.
As a young man, Bachmann served as a merchant sailor, crossing the Atlantic multiple times. He emigrated to the United States in 1902 and earned his medical degree at the top of his class from Jefferson Medical College in Philadelphia in 1907. He stayed at this Medical College as a demonstrator and physiologist. In 1910, he joined Emory University in Atlanta. Between 1917 -1918 he served as a medical officer in the US Army. He retired from Emory in 1947 and continued his private medical practice until his death in 1959.
On the personal side, Bachmann was a man of many talents: a polyglot, he was fluent in German, French, Spanish and English. He was a chef in his own right and occasionally worked as a chef in international hotels. In fact, he paid his tuition at Jefferson Medical College, working both as a chef and as a language tutor.
The intrinsic cardiac conduction system was a major focus of cardiovascular research in the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries. The atrioventricular (AV) node was discovered and described by Sunao Tawara and Karl Albert Aschoff in 1906, and the sinoatrial node by Arthur Keith and Martin Flack in 1907.
While the connections that distribute the electrical impulse from the AV node to the ventricles were known through the works of Wilhelm His Jr, in 1893 and Jan Evangelista Purkinje in 1839, the mechanism by which electrical impulses spread between the atria remained uncertain.
In 1916 Bachmann published a paper titled “The Inter-Auricular Time Interval” in the American Journal of Physiology. Bachmann measured activation times between the right and left atria and demonstrated that interruption of a distinct anterior interatrial muscular band resulted in delayed left atrial activation. He concluded that this band constituted the principal route for rapid interatrial conduction.
Subsequent anatomical and electrophysiological studies confirmed the importance of the structure described by Bachmann, which came to bear his name. Bachmann’s bundle is now recognized as a key determinant of atrial activation patterns, and its dysfunction is associated with interatrial block, atrial fibrillation, and abnormal P-wave morphology. His work remains foundational in both basic cardiac anatomy and clinical electrophysiology.
Sources and references
1. Bachmann G. “The inter-auricular time interval”. Am J Physiol. 1916;41:309–320.
2. Hurst JW. “Profiles in Cardiology: Jean George Bachmann (1877–1959)”. Clin Cardiol. 1987;10:185–187.
3. Lemery R, Guiraudon G, Veinot JP. “Anatomic description of Bachmann’s bundle and its relation to the atrial septum”. Am J Cardiol. 2003;91:148–152.
4. "Remembering the canonical discoverers of the core components of the mammalian cardiac conduction system: Keith and Flack, Aschoff and Tawara, His, and Purkinje" Icilio Cavero and Henry Holzgrefe Advances in Physiology Education 2022 46:4, 549-579.
5. Knol WG, de Vos CB, Crijns HJGM, et al. “The Bachmann bundle and interatrial conduction” Heart Rhythm. 2019;16:127–133.
6. “Iatrogenic biatrial flutter. The role of the Bachmann’s bundle” Constán E.; García F., Linde, A.. Complejo Hospitalario de Jaén, Jaén. Spain
7. Keith A, Flack M. The form and nature of the muscular connections between the primary divisions of the vertebrate heart. J Anat Physiol 41: 172–189, 1907.
"Clinical Anatomy Associates, Inc., and the contributors of "Medical Terminology Daily" wish to thank all individuals who donate their bodies and tissues for the advancement of education and research”.
Click here for more information
- Details
This article is part of the series "A Moment in History" where we honor those who have contributed to the growth of medical knowledge in the areas of anatomy, medicine, surgery, and medical research.
Hippocrates of Cos (460 BC - 370 BC). A Greek physician, Hippocrates was born on the Greek island of Cos (Kos) c. 460BC. Considered the "Father of Medicine" he removed Medicine from the realms of superstition and magic. He was the first to record medical writings and is considered the first one to use and maintain proper medical terminology. There are many writing attributed to Hippocrates, but there is no assurance that these were actually written by Hippocrates himself. Hippocrates changed the art of medical diagnosis by replacing supernatural precepts with observation-based methodology. Natural, rather than supernatural causes, would from here on explain all disease processes, what was known as Rational Medicine.
He is known for having set the oath that governs medical principles, the Hippocratic Oath, although there are many authors that contend that this oath was written long time after he died.
Sources:
1. "Hippocrates himself" JAMA. 1968;204(12):1138-1139
2. "Hippocrates: father of medicine" Tan, S Y (01/01/2002). Singapore medical journal(0037-5675), 43(1), p.5.
- Details
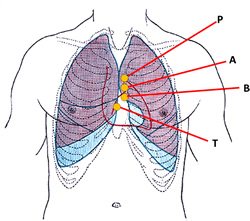
Anterior view of the thorax, showing surface
relations of bones, lungs (purple), pleura (blue),
and heart (red outline).
P. Pulmonary valve. A. Aortic valve.
B. Bicuspid valve. T. Tricuspid valve
This is a combined word arising from terms [atrium], [ventricle], and [sulcus]. For the etymology of each word, click on the corresponding link.
The atrioventricular sulcus, also know as the "coronary groove" or "coronary sulcus" is an evident incomplete groove between the atria and ventricles of the heart. It is complete posteriorly and is separated anterosuperiorly by the roots of the aorta and the pulmonary trunk. It contains the right coronary artery on the right side, and the circumflex artery on the left side, hence the name "coronary groove". These coronary arteries are not visible as they are usually covered by the epicardium and subepicardial fat.
The atrioventricular sulcus (and the corresponding coronaries) are also in relation to the deeper situated atrioventricular (AV) valves, the tricuspid valve on the right; and the mitral or bicuspid valve on the left side. The accompanying image depicts the location of the AV valves, and therefore the location of the AV sulcus. The image is an anterior view of the thorax, showing surface relations of bones, lungs (purple), pleura (blue), and heart (red outline). P. Pulmonary valve. A. Aortic valve. B. Bicuspid valve. T. Tricuspid valve
Sources:
1. "The Origin of Medical Terms" Skinner, HA 1970 Hafner Publishing Co.
2. "Medical Meanings - A Glossary of Word Origins" Haubrich, WD. ACP Philadelphia
3 "Tratado de Anatomia Humana" Testut et Latarjet 8 Ed. 1931 Salvat Editores, Spain
4. "Anatomy of the Human Body" Henry Gray 1918. Philadelphia: Lea & Febiger
Image modified by CAA, Inc. Original image by Henry Vandyke Carter, MD., courtesy of bartleby.com
- Details
This article is part of the series "A Moment in History" where we honor those who have contributed to the growth of medical knowledge in the areas of anatomy, medicine, surgery, and medical research.

Galen of Pergamum
Galen of Pergamon (129AD - 200AD). A Roman physician of Greek origin, Galen is a seminal character in Medicine and Physiology for the ages. He has been known as Galen, Galenus, Aelius Galenus, Claudius Galenus, Claudius Clarissimus Galen, and Galen of Pergamus. He was born in 129 A.D. in a Roman-Greek community in Pergamum (today's Turkey). As a very young man, he studied Medicine at the Pergamum temple of Asclepius. After traveling for additional studies, Galen obtained the appointment of "physician to the gladiators" back at this hometown of Pergamum.
The post required of him to study and develop hygiene, preventive medicine, as well as dealing with the gladiator's injuries. The horrible wounds allowed him to observe and study human anatomy and develop incredible skills at treating battle wounds. Galen traveled to Rome, where he was appointed Physician to the Emperor Marcus Aurelius.
Galen performed human and animal anatomical dissections, writing over 300 medical, pharmaceutical, and philosophical treatises in Greek, many of which were translated into other languages, especially Latin and Arabic.
Even though most of the original books were lost, the translations and interpretations of Galen's work have survived until today. His teachings and dictums were considered undisputable for over 1,500 years. In fact, in Medieval times and early Renaissance doubting Galen's teachings was considered heresy!
Galen's name is preserved in the eponymical "Vein of Galen", the great central cerebral vein.
Sources:
1. "Claudius Galenus of Pergamum: Surgeon of Gladiators. Father of Experimental Physiology" Toledo-Pereyra, LH; Journal of Investigative Surgery, 15:299-301, 2002
2. "Galen: history’s most enduring medic" Tan, SY; Singapore Med J 2002:3 (43):116 –117
3. "Galen and His Anatomic Eponym: Vein of Galen" Ustun, C.; Clinical Anatomy 17:454–457 (2004)
Original image in the public domain, courtesy of the National Library of Medicine
- Details
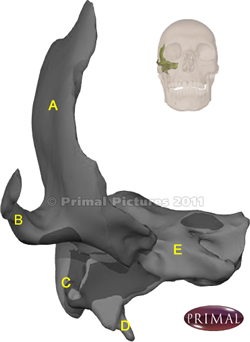
The temporal bone is a complex bone composed of several regions. The image shows an anterior view of the right temporal bone. To see the location of the bone, look at the inset that shows by transparency the location of the bone. Click on the image for a larger picture.
A. Squamous portion: From the Latin [squama], and meaning "scale-like", this portion of the bone is very thin, articulating with the parietal and sphenoid bones.
B. Zygomatic process: an anterior extension that articulates with the corresponding temporal process of the zygomatic bone.
C. Mastoid process: A Greek term from [-mast-] meaning breast, and the suffix [-oid] meaning "similar to".
D. Styloid process: Another Greek term from [stylos] meaning a "pillar", but also a "pen", therefore "shaped or similar to a pen". This is a slender and long inferior bony process. Close to the syloid process there are other processes, the pterygoid processes.
E. Petrous process: From the Latin [petrus] meaning "rock". The petrous process contains the components of the external auditory canal, the middle and inner ear, and a large canal through which passes the internal carotid artery.

First image modified from the original: "3D Human Anatomy: Regional Edition DVD-ROM." Courtesy of Primal Pictures.
Animation via Wikimedia Commons, public domain. Polygon data generated by Database Center for Life Science (DBCLS), CC BY-SA 2.1 JP.
- Details
This term has combined Greek components. The prefix [ect-] comes from [ectos], meaning "outside", and the root term [-top-] from [topos], meaning "place or location". The suffix [-ic] of course means "pertaining to". The word [ectopic] then means "outside its (normal) place or location".
The words has several uses. As an example, in atrial fibrillation, the atria of the heart will depolarize in abnormal or ectopic locations, causing a dysrhythmia. Another common use is in endometriosis, where there are abnormal or ectopic implantation sites of endometrium.
- Details
This article is part of the series "A Moment in History" where we honor those who have contributed to the growth of medical knowledge in the areas of anatomy, medicine, surgery, and medical research.
Oliver W. Holmes Sr. (1809-1894). American physician, writer, and poet, Oliver Wendell Holmes Sr. was born in 1809 in Cambridge, MA. He started his studies in law, but soon turned to Medicine, studying part of his time in Paris. In 1843 he joined the fight against "puerperal fever", for which he was mocked, but he stood his ground on principle. A gifted writer, he published several books on essays, biography, and poetry. He was Dean of the Harvard Medical School. He received several honorary doctorates in Law and letters from Harvard and Cambridge. Little known is his contribution to Medicine by the coining of the terms "anesthesia" and "anesthetic", and that he was the father of a Supreme Court Judge, Justice Oliver Wendell Homes Jr.
The Journal of Clinical Anatomy published an article on Oliver W. Holmes Sr. profiling his many accomplishments.
Original image courtesy of www.nndb.com.
Sources:
1. "The Origin of Medical Terms" Skinner, H.A.(1970)
2. "Oliver Wendell Holmes, Sr. (1809–1894): Physician, jurist, poet, inventor, pioneer, and anatomist" Tubbs, RS et al, Clin Anat 25:8; 992-997 (2012)