The term “Bachmann’s bundle” refers to an eponymic structure associated with Jean George Bachmann (1877-1959) a French physician and physiologist. The proper anatomical term for this structure is “interatrial bundle” (Lat. fasciculus interatrialis).
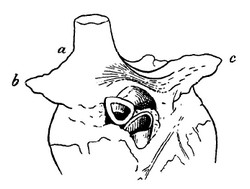
In 1916 Bachmann published a paper titled “The Inter-Auricular Time Interval” in the American Journal of Physiology. He measured activation times between the right and left atria and demonstrated that interruption of this distinct anterior interatrial muscular band resulted in delayed left atrial activation. He concluded that this band constituted the principal route for rapid interatrial conduction. The image, from his original publication, shows a dog’s heart with Bachmann’s bundle.
Bachmann’s bundle is a broad, flat band of atrial myocardium that crosses the superior aspect of the interatrial sulcus. It extends from the right atrium close to the junction of the right atrial appendage and the superior vena cava, and courses leftward across the interatrial groove to insert into the base of the left atrial appendage and the anterosuperior left atrial wall. The bundle is well-delineated and in most cases, a fine fatty layer is interposed between the underlying myocardium and the bundle.
This bundle contains predominantly longitudinally oriented myocardial fibers, aiding in fast passage of the electrical depolarization from the right atrium to the left atrium. This explains why, under normal conditions, the left atrium contracts only milliseconds after the right atrium. Bachmann's bundle is one of the components of the cardiac conduction system, and forms part of the specialized bundles of myocardial tissue that take the electrical impulses from the sinoatrial node to the atrioventricular node and the left atrium,
When Bachmann’s bundle is intact, left atrial activation is almost simultaneous with the right atrium. If it is damaged, it can cause varying degrees of interatrial block (IAB), and electrical conduction must proceed through other less effective pathways, resulting in atrial dyssynchrony and altered cardiac rhythm. Advanced IAB is strongly associated with atrial fibrillation, left atrial mechanical dysfunction, and increased risk of stroke even in sinus rhythm.
IAB can be caused by fibrosis, fatty infiltration, atrial dilation, aging, ischemia, and iatrogenic damage in prior cardiac surgery or ablation. All these preferentially affect the anterosuperior interatrial region, explaining the bundle’s vulnerability.
There are anatomical variations of Bachmann's bundle. In some cases, the bundle is separated from the atrial wall by epicardial fat, and in some cases it hugs the surface of the atria. In this last instance the bundle is more susceptible to damage by internal ablation in the left atrial wall. The location of the bundle can also vary.
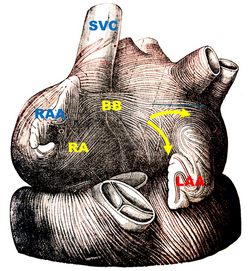
Bachmann’s bundle shows some bifurcations, helping to distribute the depolarization to the left atrium. The image, from Testut & Latarjet (1931), shows one of these bifurcations (yellow arrows). The bundle splits around the base of the left atrial appendage (LAA).
Historically, all pacemakers terminal wires have been implanted in the right atrium. but the potential dysfunction of Bachmann's bundle would require biatrial pacing, which is not used today.
Sources and references
1. Bachmann G. “The inter-auricular time interval”. Am J Physiol. 1916;41:309–320.
2. Hurst JW. “Profiles in Cardiology: Jean George Bachmann (1877–1959)”. Clin Cardiol. 1987;10:185–187.
3. Lemery R, Guiraudon G, Veinot JP. “Anatomic description of Bachmann’s bundle and its relation to the atrial septum”. Am J Cardiol. 2003;91:148–152.
4. Antonio Bayés de Luna, Albert Massó-van Roessel, Luis Alberto Escobar Robledo, The Diagnosis and Clinical Implications of Interatrial Block, European Cardiology Review 2015;10(1):54–9
5. Knol WG, de Vos CB, Crijns HJGM, et al. “The Bachmann bundle and interatrial conduction” Heart Rhythm. 2019;16:127–133.
6. “Iatrogenic biatrial flutter. The role of the Bachmann’s bundle” Constán E.; García F., Linde, A.. Complejo Hospitalario de Jaén, Jaén. Spain
7. "Tratado de Anatomia Humana" Testut et Latarjet 8th Ed. 1931 Salvat Editores, Spain
8. 4. Rigamonti F, Shah DC. "Bachmann Bundle Block Occurring During Radiofrequency Ablation at the Inter-Atrial Septum" J Clin Med. 2012;15(9):263.
9. Zhang Y, Wu F, Gao Y, Wu N, Yang G, Li M, Zhou L, Xu D, Chen M. "Bachmann bundle impairment following linear ablation of left anterior wall: impact on left atrial function". Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2022 Jan;38(1):41-50
10. Platonov, PG; Mitrofanova, L, et al.Substrates for intra-atrial and interatrial conduction in the atrial septum: Anatomical study on 84 human hearts Heart Rhythm,(2008)5:8,1189-1195.