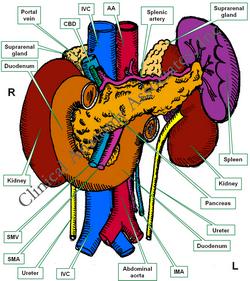
The duodenum is a mostly retroperitoneal organ, part of the digestive tract, and the most proximal portion of the small intestine. This organ is approximately 10 inches in length (24.5 cm). It starts at the pylorus of the stomach, has a "C" shape, curving around the head and the neck of the pancreas, to end at the duodenojejunal junction.
The duodenum is described as having four segments of differing length, usually named numerically:
- First segment: about two inches in length, it is dilated and called the "duodenal ampulla", or "superior duodenum"
- Second segment: about three inches in length, it receives bile and pancreatic juice through the hepatopancreatic ducts and ampullae. It is also called the "descending duodenum"
- Third segment: about four inches in length, it crosses the midline, and is also known as the "horizontal" or "transverse duodenum"
- Fourth segment: one inch in length, this is the shortest segment, it ascends towards the duodenojejunal junction, which is tethered to the diaphragm by a fold of peritoneum around a fibromuscular band called the "ligament of Treitz". At this point the retroperitoneal duodenum becomes the intraperitoneal jejunum. This fourth segment is also called the "ascending duodenum"
The name of the organ is interesting. Most textbooks claim that is originates from the Latin [duodeni], meaning "twelve". The fact is that the duodenum was originally named in Greek [δώδεκα δάχτυλαν] meaning "twelve fingers". If you place both your hands together and add 1/4 of an inch to each side (as if you had an extra finger on each hand) that measures approximately 10 inches. The term was shortened by an incorrect translation to "twelve" by Gerard of Cremona (1114 - 1187) who called it "duodenum", a bad translation, as twelve fingers in Latin is [duodecim digitorum].
While most of the duodenum is retroperitoneal, the first inch of the superior duodenum (first segment) is intraperitoneal as it shares a small portion of the lesser omentum with the stomach and liver.
Sources:
1. "Clinically Oriented Anatomy" Moore, KL. 3r Ed. Williams & Wilkins 1992
2. "The origin of Medical Terms" Skinner, AH, 1970
Image property of: CAA, Inc. Artist: Dr. E. Miranda