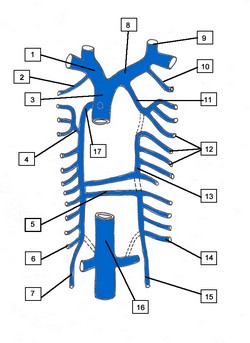
The azygos venous system drains the posterior aspect of the thorax via the posterior intercostal veins It also connects the vascular territories of the superior vena cava and the inferior vena cava, and is the superior continuation of the lumbar veins. The azygos system was first described by Bartolomeo Eustachius (c1500 - 1574).
The name azygos comes from the Greek [ζεύγος] and means “unyoked” or better “asymmetrical”. This system is different on each side of the body, also having important anatomical variations.
The azygos vein (Lat: vena azygos major) is the larger vein of the azygos system and is found on the right side of the body. It begins at the level of the first or second lumbar vertebra as a continuation of the right ascending lumbar vein; sometimes by a branch from the right renal vein or from the inferior vena cava. It enters the thoracic cavity through the aortic hiatus of the respiratory diaphragm, and ascends along the right side of the vertebral column to level of the fourth thoracic vertebra, where it arches forward over the root of the right lung, at this point the vein is called the azygos arch, which terminates in the posterior aspect of the superior vena cava (SVC) just superior to the point where the SVC enters the pericardium.
In the thorax, the azygos vein is found to the right of the thoracic duct on the right side of the descending aorta; it lies upon the intercostal arteries and is partly covered by the parietal pleura.
The azygos vein receives the right subcostal vein, nine or ten right posterior intercostal veins, the hemiazygos vein, the accessory hemiazygos vein, the right superior intercostal vein, and several minor esophageal, mediastinal, and pericardial veins.
The left side of this system is more complex and presents with more anatomical variations. Its main component is the hemiazygos vein (Lat: vena azygos minor), also known as the left lower azygos vein. It is a continuation of the left ascending lumbar vein, and it sometimes may arise from the left renal vein and passes into the thorax usually through the left aortic crus of the respiratory diaphragm. It ascends to the level of the 7th or 8th thoracic vertebra where it crosses the midline posterior to the esophagus, descending aorta and thoracic duct to empty into the right-sided azygos vein. It receives the left subcostal vein and three to four lower posterior intercostal veins, and some esophageal and mediastinal veins.
The second component of the left azygos system is the accessory hemiazygos vein, also known as the left upper hemiazygos. This component varies in size depending on the third venous drainage component of the left posterior thoracic wall. This is the left superior intercostal vein (see attached diagram).
The accessory hemiazygos, similar to the hemiazygos vein will cross the midline posterior to the esophagus, descending aorta and thoracic duct to empty into the right-sided azygos vein. It may do so by a common vein or by a separate vein as shown in the attached diagram. If there is a common vein the hemiazygos is considered to be the inferior component and the hemiazygos is considered to be the superior component.
The left superior intercostal vein receives three or four posterior intercostal veins, and empties into the left brachiocephalic vein. In rare cases of absence of the hemiazygos vein, this left superior intercostal vein will extend as low as the fifth or sixth intercostal space.
Although not considered to be part of the azygos system, the drainage of the posterior thoracic wall is completed by the right and left supreme intercostal veins which empty the posterior aspect of the first intercostal space into the left and right brachiocephalic veins respectively.
The azygos system of veins constitute an important collateral venous circulation pathway which can be seen in action in cases of blockage of the superior or inferior vena cavæ.
Sources:
1. “Gray’s Anatomy” Henry Gray, 1918
2. "Tratado de Anatomia Humana" Testut et Latarjet 8th Ed. 1931 Salvat Editores, Spain
3. "Gray's Anatomy" 38th British Ed. Churchill Livingstone 1995
4. "Reconstructive Anatomy: A Method for the Study of Human Structure: Arnold, M WB Saunders1968
Image modified from the original from Arnold (4)