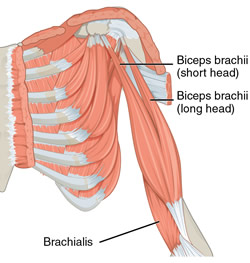
Biceps brachii muscle.
Click on the image for a larger depiction
The musculus biceps brachii is a long muscle found in the anterior, aspect of the arm and is one of the three muscles contained in the anterior compartment (flexor compartment) of the arm, the other two being the brachialis and coracobrachialis muscles. It is composed by two muscular heads, one long (lateral) , and one short (medial) that originate superiorly from separate tendons that attach to the scapula. These two heads join to form a single long, oval-shaped belly with a single tendon that crosses the elbow joint and attaches to the radius.
The short tendon of the biceps brachii passes anteromedial to the shoulder joint and attaches to the coracoid process of the scapula by way of a tendon that mixes with the tendon of the coracobrachialis muscle.
The long cylindrical tendon of the biceps brachii is found in the intertubercular (bicipital) groove (Lat: sulcus intertubercularis) of the humerus, and passes between the greater and lesser tubercles of the humerus, entering the articular cavity of shoulder joint, and continues superiorly to insert in the supraglenoid tubercle of the scapula.
The distal, common tendon of the biceps brachii courses inferiorly and attaches to the radial (bicipital) tuberosity of the radius. There is a well-defined bursa between the radial tuberosity and the biceps brachii tendon that allows for movement of the tendon.
Also, a flat, fascial extension of the tendon, known as the bicipital aponeurosis extends inferomedially to blend with the antebrachial aponeurosis that covers the epitrochlear muscles of the forearm (pronator teres, flexor carpi radialis muscles). The brachial artery passes between the tendon of the biceps brachii and the bicipital aponeurosis in the anterior aspect of the elbow joint.
The biceps brachii crosses both the shoulder and the elbow join. As such, its functions will depend on which joint is fixed and which one is not. This muscle flexes the elbow, supinates the forearm, and flexes the shoulder.
It is innervated by the musculocutaneous nerve (C5,D6) which is a branch of the brachial plexus. It receives arterial supply by way of muscular branches that arise from the brachial artery.
The name of the muscle literally means "two heads" as the prefix "bi" means "two" and the Latin term "-ceps" means "head".
Note: Because the long and the short head of the biceps brachii attach to different locations of the scapula, some authors and Internet websites say that there are 18 muscles that attach to the scapula. I do not agree, as the biceps brachii is a single muscle that happens to have to separate attachments to the scapula. It would be different if this article was titled "Name the 18 separate muscular attachment points of the scapula". Dr. Miranda
The image is modified from the original via Wikimedia. Public domain. Animated image below by Wikimedia Commons - Anatomography [CC BY-SA 2.1 following Creative Commons attributes.
 Sources:
Sources:
1. “Gray’s Anatomy” Henry Gray, 1918
2. "Tratado de Anatomia Humana" Testut et Latarjet 8th Ed. 1931 Salvat Editores, Spain
3. "Gray's Anatomy" 42nd British Ed. Churchill Livingstone 2021
4. “An Illustrated Atlas of the Skeletal Muscles” Bowden, B. 4th Ed. Morton Publishing. 2015
5. "Trail Guide to The Body" 4th. Ed. Biel, A. Books of Discovery. 2010



