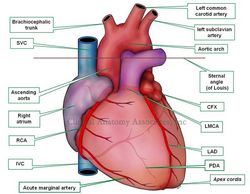
The right coronary artery (RCA) is one of the two branches that arises from the ascending aorta and provide blood supply to the heart. The RCA begins at the coronary ostium, situated usually within the right sinus of Valsalva found in the aortic valve, one of the semilunar valves of the heart.
The RCA gives off in its initial course two arteries: the conus artery, which gives blood to the conus arteriosus, the outflow tract of the right ventricle, and the artery to the sinoatrial (SA) node, a component of the conduction system of the heart.
The RCA descends in the atrioventricular sulcus, giving off a series of small right ventricular branches and a couple of small right atrial branches, it then bends around the acute margin (margo acutus) and passes to the posterior surface of the heart. Just before the RCA bends posteriorly, it will give off the acute marginal artery, usually a thin, longer branch that extends towards the cardiac apex.
In its posterior trajectory the RCA gives off a couple of small posterior right ventricular arteries and then ends at the crux cordis, where the RCA gives off the posterior interventricular artery, commonly known as the posterior descending artery (PDA). The RCA will also give off the posterolateral artery, which, situated in the atrioventricular sulcus, extends the vascular territory of the RCA into the region of the left ventricle. This origin of the PDA from the RCA is subject to anatomical variation, which gives origin to the concept of coronary dominance.
Arising from the terminal portion of the RCA (sometimes from the posterolateral artery) is the artery to the atrioventricular (AV) node, another component of the conduction system of the heart. It is easily understood that stricture or stenosis of the RCA (depending on location) can then lead to damage of the conduction system of the heart.
Human heart and coronary artery anatomy and pathology are some of the many lecture topics developed and presented by Clinical Anatomy Associates, Inc.
Image property of: CAA.Inc.Artist: Victoria G. Ratcliffe