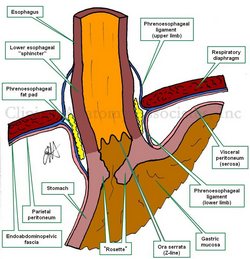
UPDATED: The esophageal hiatus is one of the seven hiatuses found in the respiratory diaphragm allowing passage of structures between the thorax and abdomen. As it name implies, the esophageal hiatus is the passageway for the esophagus. It also allows passage of the anterior and posterior vagus nerves, (CN X).
The hiatus is bound by two muscular crura, both of which arise from the right tendinous aortic crus. Since the intraabdominal pressure is higher than the intrathoracic pressure, there is a series of structures at the phrenoesophagogastric junction to close the esophageal hiatus.
The infradiaphragmatic parietal peritoneum reflects off the diaphragm towards the stomach to form its serosa layer (visceral peritoneum). At the same time the infradiaphragmatic fascia, also known as the endoabdominopelvic fascia, splits into two components or limbs. These are the superior and inferior phrenoesophageal ligaments or phrenoesophageal membranes. (the root [-phren-] means "diaphragm"). These phrenoesophageal ligaments create a disc-like plug between the abdomen and the thorax. This "plug" is reinforced by a circular infradiaphragmatic fat pad. The phrenoesophageal ligaments are reinforced on their thoracic aspect by the endothoracic fascia.
The lower esophagus has a dilation (evident in the image) called the "esophageal ampulla", in relation to this dilation the circular muscle layer of the esophagus slightly thickens creating the so-called "lower esophageal sphincter". This area is not a true anatomical sphincter, but rather is a functional sphincter.
The esophagogastric mucosal junction shows a marked transition in the shape of a wavy line. This is called the Z-line or the ora serrata. Extensions of the gastric mucosa and submucosa inferior to the ora serrata create a valve-like flap called the "gastroesophageal flap valve". When viewing this mucosal flap through and endoscope, it looks corrugated and flower-like, hence it is also called the "rosette".
The congenital or pathological dilation of the esophageal hiatus can predispose to esophageal hiatus hernia.
Sources:
1 "Tratado de Anatomia Humana" Testut et Latarjet 8 Ed. 1931 Salvat Editores, Spain
2. "Anatomy of the Human Body" Henry Gray 1918. Philadelphia: Lea & Febiger
Original image by Dr. E. Miranda