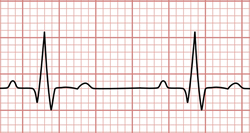
Sinus rhythm electrocardiogram
Sinus Rhythm (SR), also known as Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR) is the term used to denote normal cardiac activity. A normal beating heart is in sinus rhythm.
In the normal beating of the heart the left and right atria contract followed by the contraction of the left and right ventricles. These atrial and ventricular contractions are separated by a lag time of 1/10th of a second which allows the atria to relax (atrial diastole) while the ventricles contract (ventricular systole). The addition of the normal action of the four heart valves (tricuspid, mitral, aortic, and pulmonary) allows the heart to work as a blood pump and circulate blood within the heart and through the body and lungs.
SR is coordinated by a complex binary conduction system. The first part of the conduction system is composed of heart muscle cells (cardiomyocytes) which are characterized by automaticity. It is important to state here something that is known, but many times ignored: This portion of the conduction system is not composed of nerves... it is formed by specialized cardiac muscle cells! The description of this cardiomyocyte-based system can be read in a separate article here.
The second component of the conduction system is the cardiac autonomic nervous system (CANS), which acts as a moderator (accelerating or slowing) the cardiomyocyte-based conduction system. A separate article will be written soon and linked here. Suffice it to say (for now) that the CANS has two components, an extrinsic component formed by nerves and ganglia outside the heart, and an intrinsic component of nerves and ganglia that forms a complex network within the superficial aspect of the heart muscle and fat surrounding the heart. These are the ganglionated plexuses, and their dysfunction can cause abnormal heart rhythm.
When these two components and their thousands of cardiac muscle cells, ganglia, and nerves are working property, the heart is in sinus rhythm, and beats between 60 to a 100 times per minute.
Personal note: The term Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR) is redundant. By definition, if the heart is in SR, it is normal. On the other hand, the term Abnormal Sinus Rhythm is also not correct… if the heartbeat is abnormal, the heart is not in SR! (Dr. Miranda)