|
The serratus anterior or serratus magnus is a is a wide, thin muscle sheet situated on the posterolateral aspect of the thorax and extends between the ribs and the scapula. It is formed by well-defined separate muscular digitations that originate in the external surface and superior aspect of the first superior eight (or nine) ribs. These originating fibers also arise from the fasciae covering the intercostal muscles. This is especially true for the first or most superior digitation which arises from the first and second rib and the intervening external intercostal fascia. These digitations cover the lateral aspect of the thorax, pass deep to the scapula and converge to insert on the deep aspect of the medial border of the scapula. Some of its fibers may even hug the medial border of the scapula and insert on its anterior aspect. The first digitation is inserted into a triangular area on the ventral surface of the medial scapular angle. The next two digitations spread out to form a triangular sheet, the base of which is directed posteriorly and is inserted into nearly the whole length of the ventral surface of the vertebral border. The lower five or six digitations converge to form a fan-shaped mass, the apex of which inserts into a triangular impression on the ventral surface of the inferior scapular angle. The lower four slips of the serratus anterior interdigitate with the superior five muscular slips of the external oblique muscle. |
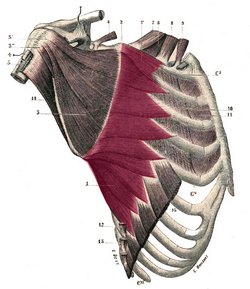 Serratus magnus muscle. Click on the image for a larger depiction |
| This muscle receives its nerve supply from the long thoracic nerve, (ventral rami of C5-C7), arising from the roots of C5, C6, and C7 (sometimes absent) of the brachial plexus
The word “serratus” derivates from the Latin word [serro] meaning “saw”. Serratus means “serrated” referring to the multiple tooth-like anterior digitations of the muscle. The plural form for "serratus" is " serrati". The Latin term “magnus” means “great”, “large”, or “mighty”. It points to the fact that this is the largest of three muscles that carry the same name “serratus”. The other two are the serratus posterior superior and the serratus posterior inferior. The serratus anterior is one of the 17 muscles that attach to the scapula. Note: The image shown in this article is from “Gray’s Anatomy” by Henry Gray (1918) which is in the public domain. It depicts the serratus anterior in situ and shows the scapula retracted posteriorly. The scapula is covered on its internal aspect by the subscapularis muscle (number 3 in the image). A better image can be found in “An Illustrated Atlas of the Skeletal Muscles” by Bowden (2015) which we cannot publish for copyright reasons. Sources: Image modified from the original by Henry VanDyke Carter, MD. Public domain |
|
| Back to MTD Main Page | Subscribe to MTD |